Why Banks Offer Different Rates to Similar Profiles
|
You and your colleague have similar salaries, similar CIBIL scores, and work in the same city. Yet when both of you apply for a loan, the interest rates offered are different. This often confuses borrowers. Why do banks offer different rates to seemingly similar profiles? In 2026, loan pricing is highly data-driven. Interest rates are influenced by multiple visible and invisible factors beyond basic income and credit score. At Saarathi.ai, we have observed that many borrowers assume loan rates are fixed or standardized. In reality, risk-based pricing models determine the final offer. Understanding how lenders calculate interest rates can help you negotiate better and choose smarter.
How Loan Interest Rates Are Determined
Interest rates are based on risk assessment.
Banks and NBFCs evaluate:
CIBIL score
Income stability
Employer category
Existing debt
Loan amount
Tenure
Repayment history
Internal risk models
Even small differences in these factors can lead to rate variation.
Risk-Based Pricing Explained
Most lenders follow risk-based pricing.
This means:
Lower perceived risk = lower interest rate
Higher perceived risk = higher interest rate
Two borrowers may appear similar on the surface but differ in deeper data points.
Factor 1: Credit Score Range, Not Just Score
A score of 750 and 780 are both good. But internally:
780 may qualify for premium rate
750 may fall into slightly higher risk band
Banks divide scores into internal buckets.
Even 10 to 20 point difference can change pricing.
Factor 2: Credit Utilization Ratio
If two borrowers have same income and CIBIL score but:
Borrower A uses 20 percent of credit limit
Borrower B uses 60 percent
Borrower B may receive slightly higher interest rate due to perceived risk.
Credit utilization signals financial stress.
Factor 3: Employer Category and Industry
Banks classify employers into risk tiers.
For example:
Government employees
Large multinational companies
Mid-sized private firms
Self-employed professionals
Stability perception varies.
Even within private sector, industry type matters. IT sector may be treated differently from startup-based employment.
Factor 4: Existing Loan Obligations
Debt-to-income ratio plays a major role.
Two borrowers earning Rs 1 lakh per month:
Borrower A has no existing loans
Borrower B pays Rs 35,000 in EMIs
Borrower B is riskier.
Higher debt burden can increase offered rate.
Factor 5: Loan Tenure and Amount
Longer tenure increases lender risk exposure.
Higher loan amount also increases risk.
Even with similar profiles:
Shorter tenure may attract lower rate
Higher ticket size may push rate upward
Always evaluate tenure impact carefully.
You can compare personal loan offers on Saarathi.ai to see how tenure changes affect total cost.
Factor 6: Relationship With Bank
Existing customers sometimes receive:
Preferential rates
Pre-approved offers
Lower processing fees
Your salary account relationship may influence pricing.
Factor 7: Internal Lending Strategy
Each bank has its own:
Cost of funds
Risk appetite
Growth targets
Portfolio exposure
If a bank is aggressively growing personal loans, rates may be competitive. If exposure is already high, rates may increase.
This is why two banks may offer very different rates for the same borrower.
Factor 8: Market Conditions
Interest rates also depend on:
RBI policy rates
Inflation trends
Liquidity conditions
Economic outlook
Even timing matters. A borrower applying in a rising rate environment may receive higher offer than someone who applied earlier.
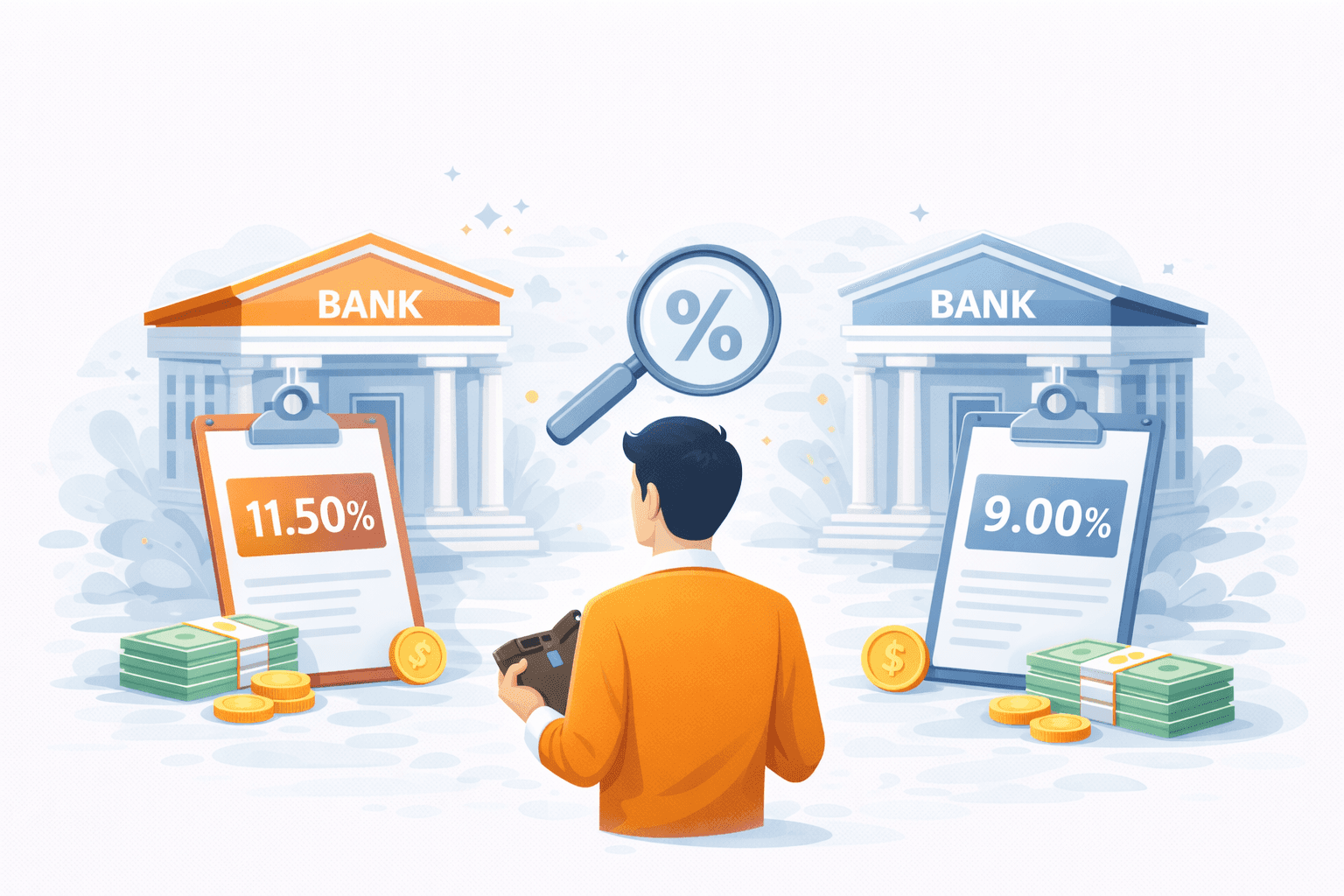
Real Scenario Example
Two salaried professionals:
Profile similarity:
Salary Rs 90,000
CIBIL score above 750
Same city
Differences:
Borrower A credit utilization 25 percent
Borrower B credit utilization 65 percent
Result:
Borrower A receives 11.5 percent
Borrower B receives 13 percent
Small behavioral differences create pricing gaps.
At Saarathi.ai, we have observed that improving even minor risk signals can reduce interest rates meaningfully.
How to Secure a Better Interest Rate
Follow these practical steps:
1. Improve Credit Score Above 780
Higher score increases negotiation power.
2. Reduce Credit Utilization Below 30 Percent
Lower utilization signals stability.
3. Reduce Existing EMIs Before Applying
Improves debt-to-income ratio.
4. Choose Optimal Tenure
Shorter tenure may reduce interest rate.
5. Compare Multiple Lenders
Instead of accepting first offer, compare transparently.
On Saarathi.ai, our Saarathi Recommendation Engine matches you with lenders suited to your profile, helping reduce rejection risk and improve pricing transparency.
You can track offers clearly in Saarathi Bazaar dashboard before making a decision.
Does Negotiation Work?
Yes, sometimes.
If you have:
Strong CIBIL score
Stable income
Good repayment history
You can request rate revision or ask lender to match competitor offer.
However, negotiation works better when you know market rates.
Impact on Long-Term Financial Goals
Even a 1 percent difference in interest rate can significantly affect:
Total repayment
EMI amount
Financial flexibility
For large commitments like housing, comparing home loan offers on Saarathi.ai can help you choose the most competitive structure.
Myth: Same Profile Means Same Rate
This is a common misconception.
Loan pricing is dynamic and multi-layered.
Two profiles may look similar but differ in:
Spending patterns
Internal scoring
Risk segmentation
Market timing
Understanding this prevents frustration.
FAQs
1. Why did my friend get lower rate than me?
Internal risk factors, credit utilization, or debt burden may differ.
2. Can I request lower interest after approval?
You can negotiate before signing agreement.
3. Does applying to multiple banks help?
Excessive applications can hurt credit score. Compare intelligently instead.
4. Does CIBIL score alone determine rate?
No. Many other factors influence pricing.
5. Can refinancing reduce my interest rate?
Yes, if your credit profile improves or market rates decline.
Conclusion
Interest rates are not random. They reflect layered risk assessment.
Key Takeaways:
Small profile differences affect pricing.
Credit utilization and debt ratio matter.
Employer type and tenure influence rates.
Market conditions impact offers.
Comparing lenders improves your chances of better pricing.
Before accepting any loan offer, compare smartly and transparently. Explore personalized loan options on Saarathi.ai today and secure competitive rates with confidence.